Thing Around Us
There are many things around us. Some are living things. Some are non-living things. How do we differentiate them?
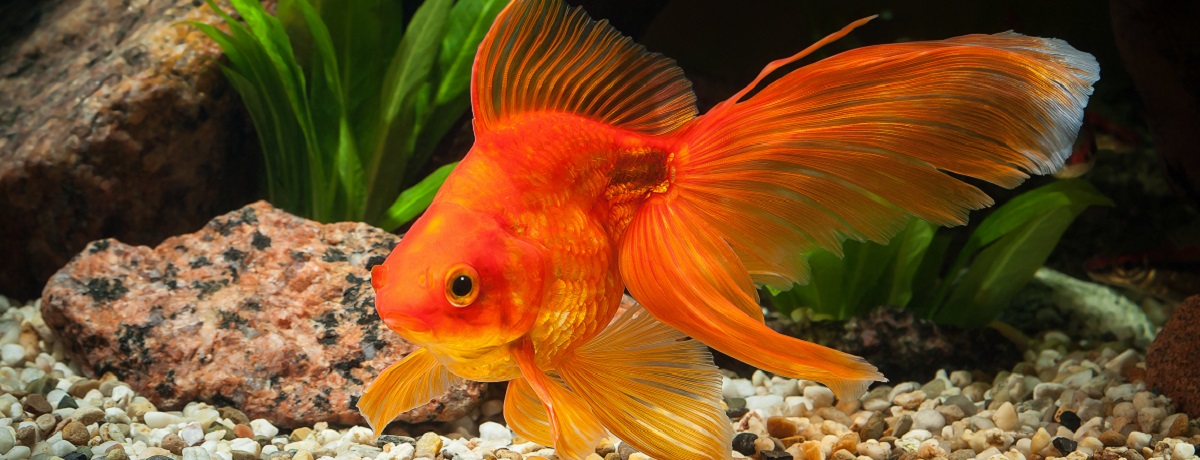
Living things are things that are alive. Humans, animals, and plants are living things. You are a living thing too! Can you make a list of living things around you? Cat, hen, rabbit, fish, flowers are the example of living things.
Cat Hen
Non-living things are things that are not alive. Here are some examples of non-living thing. Doll, color pencils, car are the example of non living things. Can you make a list of non-living things around you?
color pencils
car
doll
Needs of Living Things
All living things need air, water and food to stay alive. Without there needs for a period of time, living things will die.
We need air to breathe. We can breathe in or breathe out through the nose or mouth.
We need water to drink at least eight glasses of water every day. Lack of water can lead to dehydration — a condition that occurs when you don't have enough water in your body to carry out normal functions. Every day you lose water through your breath, perspiration, urine and bowel movements. For your body to function properly, you must replenish its water supply by consuming beverages and foods that contain water.
All living things need food. Human, animals and plants need food to get energy.
Let's Think
How do fish and aquatic plants in an aquarium get their air supply? Live plants produce oxygen and absorb carbon dioxide and ammonia in the water that fish generate.
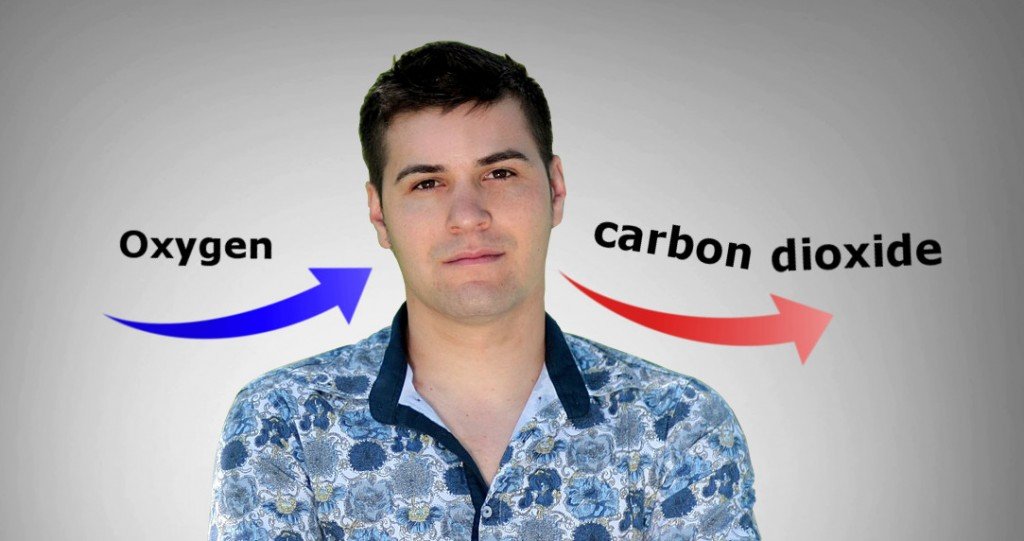
Where do humans and animals get their food from? Air flows in via our mouth or nose. The air then follows the windpipe, which splits first into two bronchi: one for each lung. The bronchi then split into smaller and smaller tubes that have tiny air sacs at their end called alveoli. We have millions of alveoli in our lungs! These sacs have thin walls—so thin that oxygen and carbon dioxide can pass through them and enter or leave our blood. The blood transports oxygen to almost every part of the body. The blood also gives the carbon dioxide a ride back to the lungs.
How do plants get their food? Plants are called producers because they make – or produce – their own food. Their roots take up water and minerals from the ground and their leaves absorb a gas called carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air. They convert these ingredients into food by using energy from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis, which means ‘making out of light’. The foods are called glucose and starch.
Characteristics of Living Things
Look around you. What are the living things and non-living things you can see? How do you differentiate living things from non-living things?
Use this interactive graphic organizer to consider whether something is living or non-living. Place each image where you think it belongs. This activity can be done individually, in pairs or as a whole class.
Activity
- Carry out this activity outside of your home
- Walk around your home and observe the surroundings.
- in this table, list things that you observed.
- Group them into living things and non-living things by placing a tick (🗸) in the correct column.
Can you describe how you grouped the things?
Living things?
Non-living things?
List the things again in the table below. Put a tick (🗸) or a cross (x) in each column.
What are the characteristics of living things that you have observed?
What is your conclusion from this activity?
Living Things Grow
What happens as living things grow? All the young of living things will grow to become bigger or taller and heavier.
.jpg)